Best Practices for International Payment in Chemical Trade
Introduction
The global chemical trade is a trillion-dollar industry connecting suppliers, exporters, and buyers across continents. But while the physical movement of goods depends on logistics and compliance, the financial backbone of trade lies in secure, timely, and reliable international payment methods. For exporters of products like PE100B, base oil SN150, solvents, and monoethylene glycol (MEG), the stakes are even higher. A single mismanaged transaction can lead to significant losses, shipment delays, or even fraud.
This article explores the best practices for international payments in the chemical and petrochemical trade, helping exporters and importers minimize risks while ensuring smooth transactions.
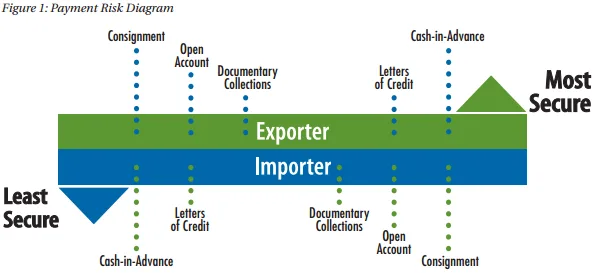
1. Common International Payment Methods in Chemical Trade
a) Letter of Credit (LC)
Most widely used in chemical exports.
Provides security for both buyers and sellers.
Requires strict compliance with documents (bill of lading, certificate of analysis, invoice).
b) Telegraphic Transfer (T/T)
Simple and fast method for advance payments or partial payments.
Riskier for sellers if 100% advance is not received.
c) Open Account
Buyer pays after receiving goods.
Used only with trusted long-term partners.
d) Documentary Collection (D/P or D/A)
Bank intermediates but does not guarantee payment.
Safer than open account but less secure than LC.
e) Escrow Services and Digital Platforms
Emerging option for small to medium transactions.
Increasingly popular in markets like UAE and Asia.
2. Risks in International Payments
Non-Payment or Delayed Payment – Buyers defaulting on payments.
Currency Fluctuations – FX volatility affecting margins in SN150 base oil or PE100B trades.
Fraudulent Transactions – Fake buyers/sellers using manipulated documents.
Compliance Risks – Violation of sanctions or trade finance regulations.
Banking Delays – Especially in high-risk markets with strict regulations.
3. Best Practices for Exporters in Chemical Trade
a) Use Letters of Credit Wisely
Confirmed LCs reduce the risk of non-payment.
Always ensure documents match LC terms precisely.
b) Diversify Payment Methods
Don’t rely solely on advance payments or open accounts.
Use a mix of LC, T/T, and escrow depending on market and buyer profile.
c) Verify Buyers and Suppliers
Always conduct due diligence (company registration, trade history).
Partner with established monoethylene glycol supplier or PE100B distributor to reduce risk.
d) Hedge Currency Risks
Use forward contracts or currency swaps to protect against volatility.
Especially important for MEG exports from the Middle East to Asia.
e) Work with Trade Finance Institutions
Partner with banks experienced in chemical trade finance.
Consider export credit agencies (ECAs) for insurance and guarantees.
4. Role of Digitalization in Payment Security
Blockchain-based trade finance is growing, ensuring transparency and speed.
Smart contracts reduce disputes by releasing payments only when terms are met.
Digital platforms in free trade zones (FTZs) like Jebel Ali simplify escrow payments.
5. Case Studies
Case 1: MEG Exporter in the Middle East
A supplier of monoethylene glycol shipped 5,000 MT to an Asian textile buyer. By using a confirmed LC, the exporter avoided risk when the buyer’s bank faced liquidity issues.
Case 2: SN150 Base Oil Trade with Africa
An African buyer requested open account payment. The exporter instead negotiated a 30% advance T/T and 70% LC, balancing trust with security.
Case 3: PE100B Supplier in Turkey
Faced with volatile currency, the exporter hedged EUR/USD exposure, securing profit despite exchange fluctuations.
6. Regional Dynamics in Payment Practices
| Region | Preferred Payment Method | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Middle East | LC & T/T | Sanctions compliance adds complexity |
| Europe | LC, Documentary Collection | High regulatory oversight |
| Asia | T/T & Escrow | Buyers often demand flexible terms |
| Africa | LC | Risk of default makes secure terms essential |
| South America | Open Account (trusted partners) | Currency volatility is a challenge |
7. Future Outlook
AI in Trade Finance: Automated compliance checks for sanctions.
More Escrow Adoption: Especially in SME-level chemical trades.
Digital Currencies: Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) may speed up cross-border payments.
Stricter Regulations: Especially in Europe for dual-use chemicals.
FAQs
Q1: What is the safest payment method for chemical exporters?
A confirmed Letter of Credit remains the most secure.
Q2: Can small exporters use LCs?
Yes, but costs may be high. Escrow or partial advance + LC is common.
Q3: How do sanctions affect payments?
Payments may be blocked if buyers or banks are blacklisted. Always conduct compliance checks.
Q4: What’s the role of insurance in payments?
Export credit insurance protects against buyer default or political risks.
Would you be looking for suppliers in Iran?
- Contact Us today and get connected with producers and export-ready logistics.
- sales@PetroExportHub.com

Related posts
Mono Ethylene Glycol (MEG) serves as a cornerstone for modern antifreeze and coolant formulations, offering reliable freezing protection and heat resi . . .
Explore Solvent 100’s specs, uses, and export opportunities from Iran. Ideal for paint, ink, and adhesive buyers in India, Turkey, UAE, and Africa. . . .
Explore everything you need to know about exporting sulphur from Iran in 2024 — including types, packaging, documents, ports, prices, and top import . . .
Explore Iran’s top ports for petrochemical exports, including Bandar Imam Khomeini, Assaluyeh, and Bandar Abbas. Compare infrastructure, accessibili . . .
Learn the key differences between polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE), their applications, advantages, and how to choose the right polymer for yo . . .
Discover how a Turkish plastics manufacturer reduced costs by 22% through importing HDPE from Iran. Real-world case study by PetroExportHub. . . .
Learn why Iran is a leading exporter of polyethylene (PE). Discover grades, global applications, and how PetroExportHub connects buyers with top suppl . . .
We are here to answer your questions....
Petro Export Hub
PetroExportHub specializes in the export of premium-grade petrochemicals, minerals, and industrial chemicals from Iran, serving international markets with reliability, transparency, and tailored logistics solutions
Tehran Office
Phone:
+989127607241
Address:
Tehran..
German Office
TEL :
+4915161647487
Address:
Heilsbronne 99441, Nuremberg
Quick Access
Quick Access
- Contact Our Sales Team
- Frequently Questions
- Shipping & Logistics
- Become a Partner
- Certificatins & Quality







